
From Palm Oil to Designer Enzymes: Frankfurt Researchers Reprogram Yeast Cells
Protein Engineering Enables Sustainable Production of Industrially Important Fatty Acids Fatty acids derived from palm oil and coconut oil are

Protein Engineering Enables Sustainable Production of Industrially Important Fatty Acids Fatty acids derived from palm oil and coconut oil are

RNA researchers Prof. Stefanie Kaiser from Goethe University Frankfurt and Dr. Eva Kowalinski from EMBL in Grenoble, France, have been

New Catalyst Developed at Goethe University Frankfurt Capable of Cleaving Strong Carbon-Fluorine Bonds – Potential Use in Pharmaceutical Production Chemists

On the afternoon of April 25, 2025, twenty doctoral candidates and postdocs from the Rhine-Main Universities (RMU) gathered at Frankfurt’s

In the future, our economy will use more and more renewable energy and therefore effective, high-capacity energy storage technologies will

Analysis of nitrogen isotope reveals the earliest known evidence of photosymbiosis in corals A research team led by researchers from

Artificial intelligence aids the discovery of new active substances in bacteria Chemical biologist Eric Helfrich, Professor of Natural Substance Genomics
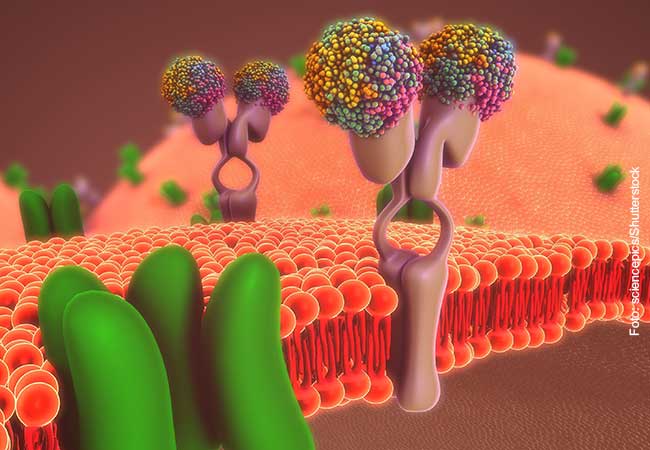
Carol Robinson, who works as a professor at Oxford University / UK, has revolutionized mass spectrometry. It is thanks to
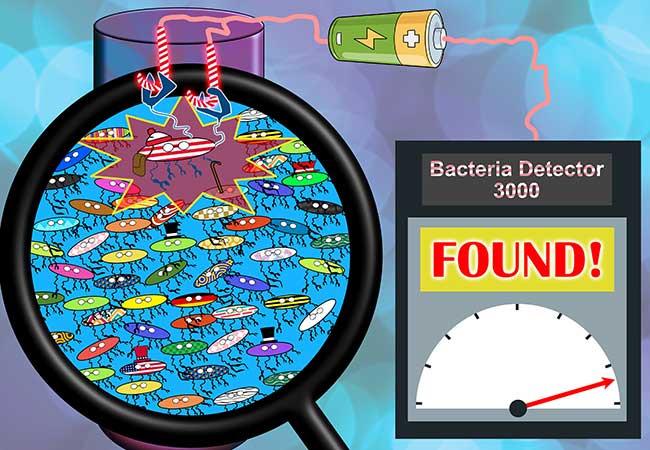
Researchers at Goethe University Frankfurt and Kiel University have developed a novel sensor for the detection of bacteria. It is

We wanted to know: Why did our scientists want to become scientists in the first place? What are they working

Prof. Ingrid Fleming, Director of Goethe University Frankfurt’s “Institute for Vascular Signalling” and a member of the Cardio-Pulmonary Institute’s (CPI)

Researchers at Goethe University Frankfurt, together with partners from the life science and pharmaceutical industries, are launching a project to
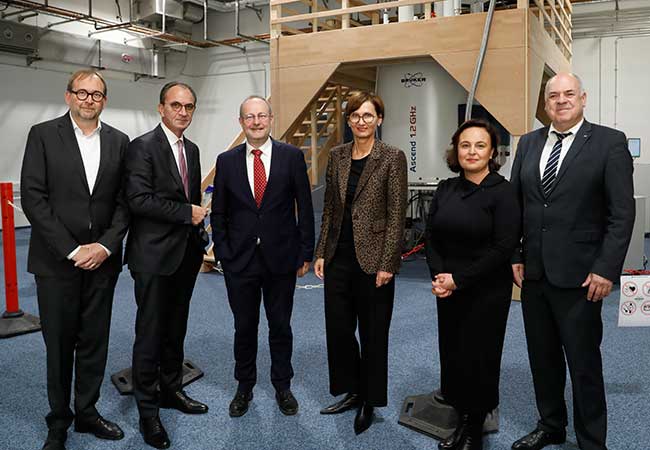

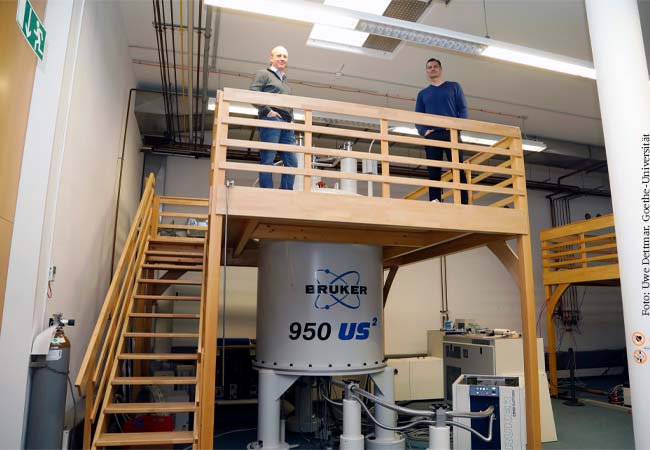
One of the world’s largest nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometers was inaugurated at Goethe University Frankfurt on October 30, 2023. The

We wanted to know: Why did our scientists want to become scientists in the first place? What are they working

Award recognizes work in the field of environmental and socio-ecological sustainability research at Goethe University Frankfurt. This year’s „Frankfurter Preis
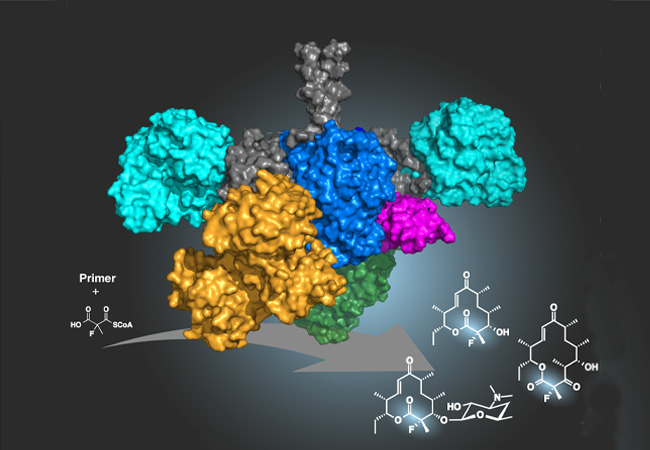
The use of the element fluorine to modify active substances is an important tool in modern drug development. A team
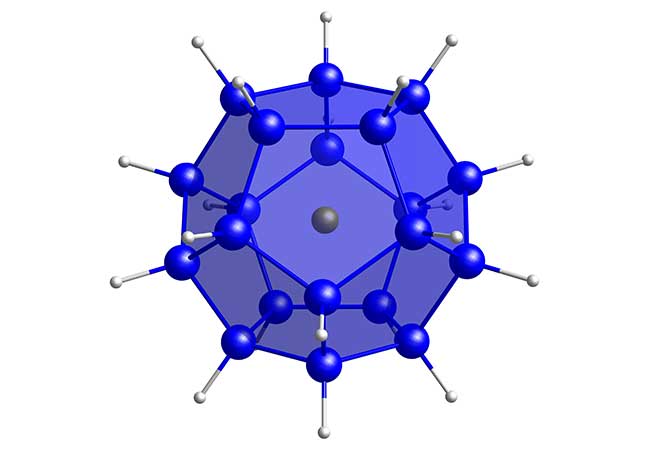
Chemists at Goethe University Frankfurt have developed two new classes of materials in the field of nanomaterials and investigated them
Certain regions of the SARS-CoV-2 genome might be a suitable target for future drugs. This is what researchers at Goethe

Researching intricate geometric and arithmetic objects is the goal of the new Collaborative Research Centre Transregio 326 (TRR 326), coordinated

For the development of drugs or vaccines against COVID-19, research needs virus proteins of high purity. For most of the
When a cell is infected, SARS-CoV-2 not only causes the host cell to produce new virus particles. The virus also
Chemical bonds within the eye-lens protein gamma-B crystallin hold the protein together and are therefore important for the function of
An ischemic stroke is an extreme disturbance of the homeostasis of brain and body. Among other things, the immune system

Catalysts with a metal-nitrogen bond can transfer nitrogen to organic molecules. In this process short-lived molecular species are formed, whose

Neanderthals behaved not so differently from us in raising their children, whose pace of growth was similar to Homo sapiens.
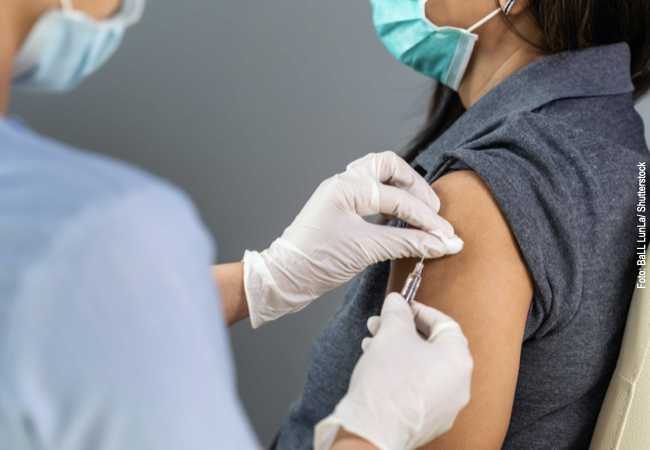
Two young chemists at Goethe University want to develop highly effective vaccines using the carrier protein dodecin. To develop their

About ten percent of Parkinson’s cases can be ascribed to mutations in the LRRK2 gene. Five research teams from the
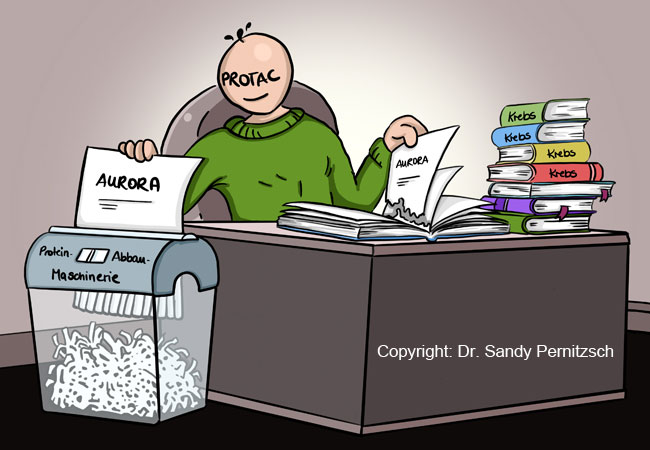

Researchers at Goethe University Frankfurt and the university of Würzburg have developed a new compound for treating cancer. It destroys
You cannot copy content of this page