
Harald Schwalbe Appointed as New Instruct-ERIC Director
Instruct-ERIC has appointed Professor Harald Schwalbe as its new Director, succeeding Professor Sir David Stuart in the role. Integrated structural

Instruct-ERIC has appointed Professor Harald Schwalbe as its new Director, succeeding Professor Sir David Stuart in the role. Integrated structural

Experts can make crucial decisions about future biodiversity management by using artificial intelligence to learn from past environmental change, according

In the winter semester of 2021/22, Flurina Schneider, scientific director of ISOE – Institute for Social-Ecological Research, will take up

The speed at which deadwood decomposes in forests depends on the climate as well as on fungi and insects. An
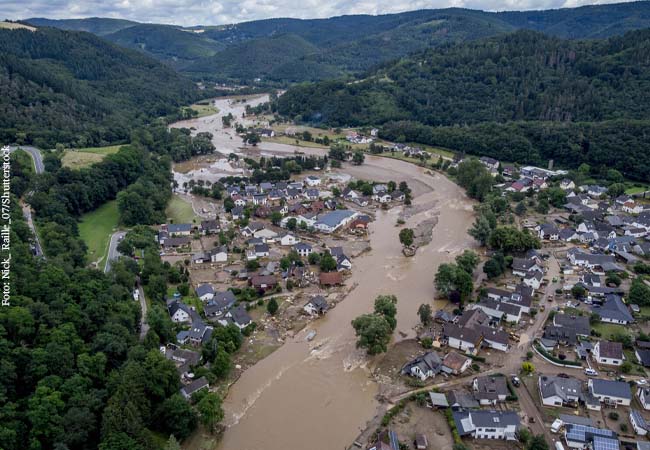

A long-term hazard from flood water is often underestimated: The raging rivers swirl up pollutants out of their sediments that
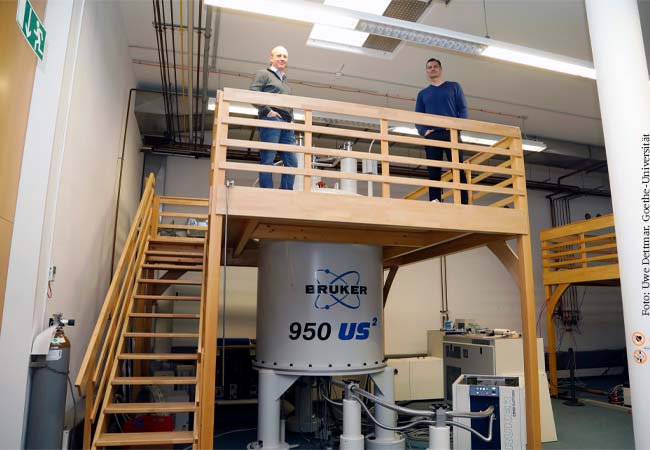

For the development of drugs or vaccines against COVID-19, research needs virus proteins of high purity. For most of the
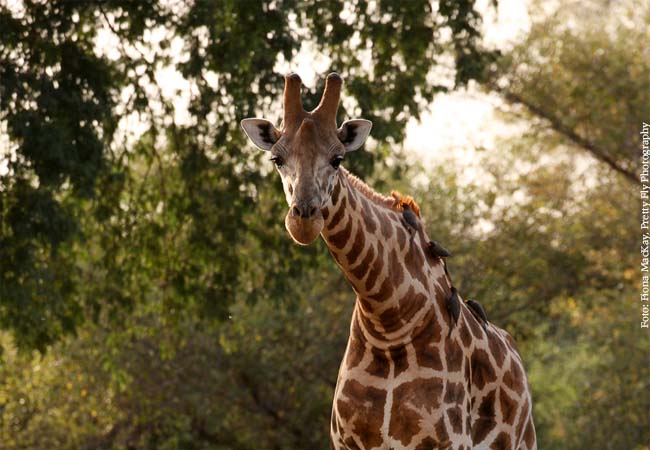

Visually, they are hardly distinguishable, but genetic analyses show: There are four distinct species of giraffe and seven subspecies. This
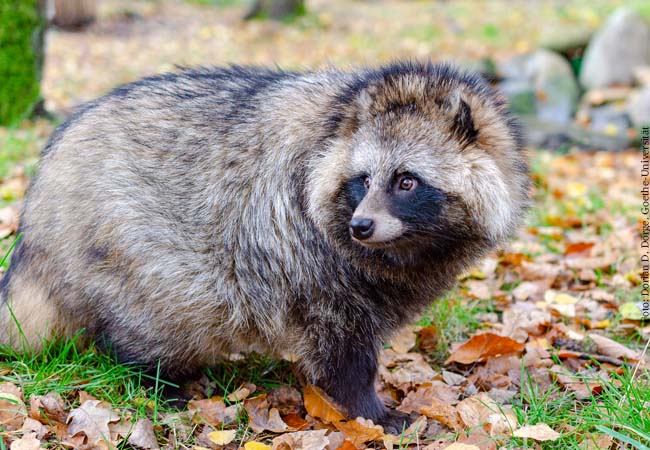

Genome of a raccoon dog sequenced for the first time – researchers see potential for transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Researchers from

While many studies take place in a petri glass in toxicology research, for some processes there is still a need

What opportunities to create trust do social conflicts offer? What happens when neutron stars merge and produce gravitational waves and
The Collaborative Research Centre 1080 was successful in the German Research Foundation’s current round of approvals and will start its
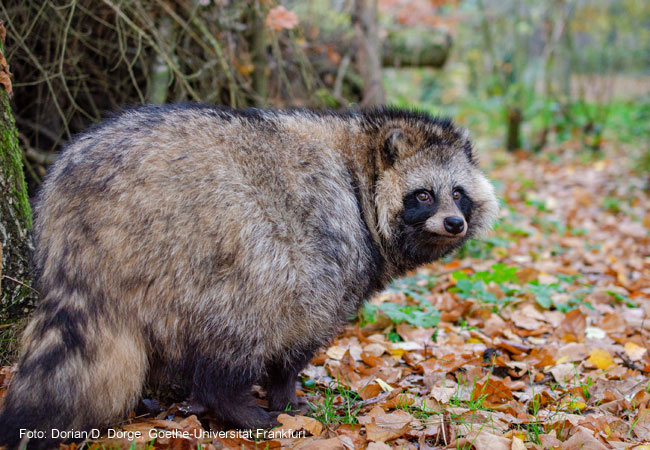

The raccoon, raccoon dog, mink and golden jackal are not native to Germany or Europe, but are increasingly spreading in
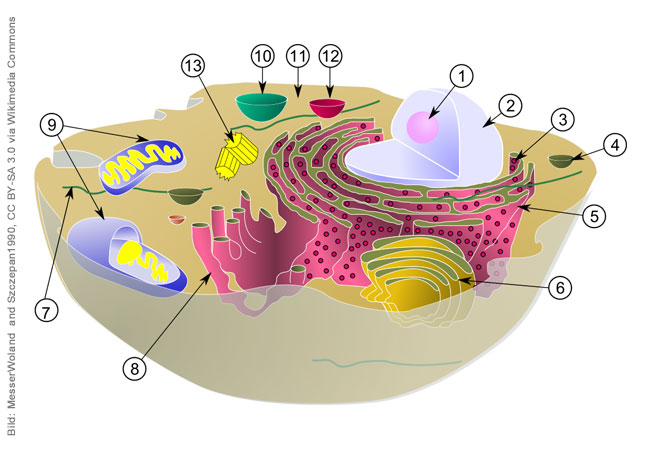
Cells of higher organisms use cell organelles to separate metabolic processes from each other. This is how cell respiration takes

So-called “bioplastics” are marketed as an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional, petroleum-based plastics. They can be made from renewable feedstock,

Researchers from Goethe University have found what is perhaps the oldest enzyme in cellular respiration. They have now been able

Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is the most common kind of cancer in children. T-ALL, a subtype that resembles T-lymphocytes, can
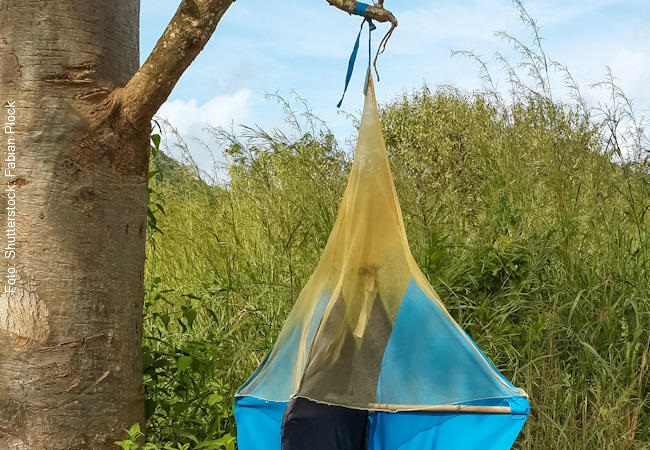

Because the tsetse fly can transmit sleeping sickness, it is commonly combatted with insecticides or caught in traps. Bioscientists at

An infection with Chagas disease is only possible in Latin America since the insect species that spread the disease only
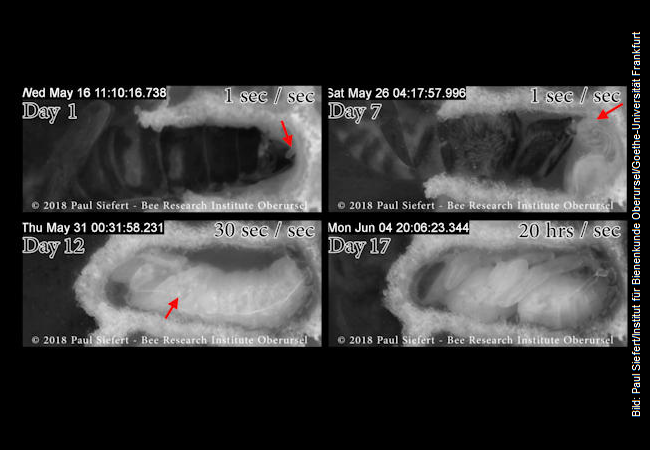
A newly developed video technique has allowed scientists at Goethe University Frankfurt at the Bee Research Institute of the Polytechnical
Bacteria of the species Thermus thermophilus possess two types of extensions on their surface (pili) for the purpose of motion
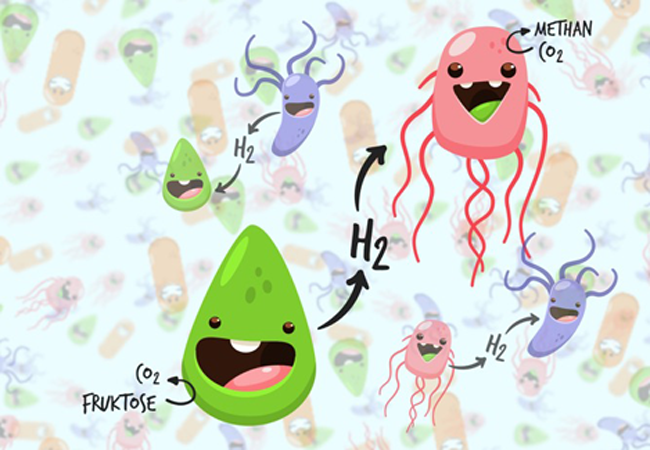
Microbiologists at Goethe University Frankfurt have discovered how the bacterium Acetobacterium woodii uses hydrogen in a kind of cycle to
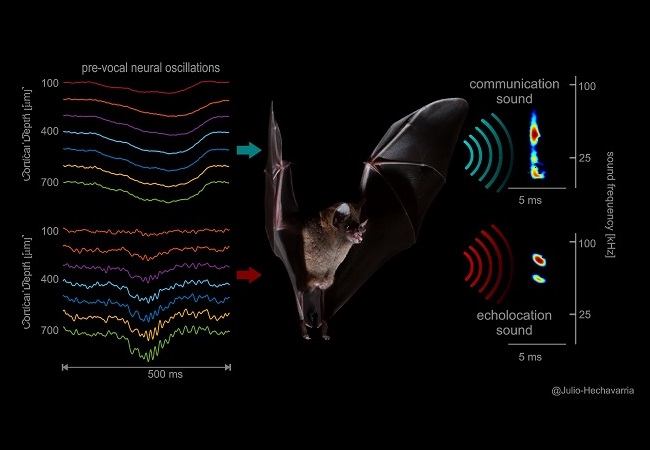
Rhythmic neural signals determine the sounds that bats make. A particular neuronal circuit in the brains of bats controls their

The formation of gametes and the first cell divisions of the fertilized egg in mammals are prone to errors. Sometimes
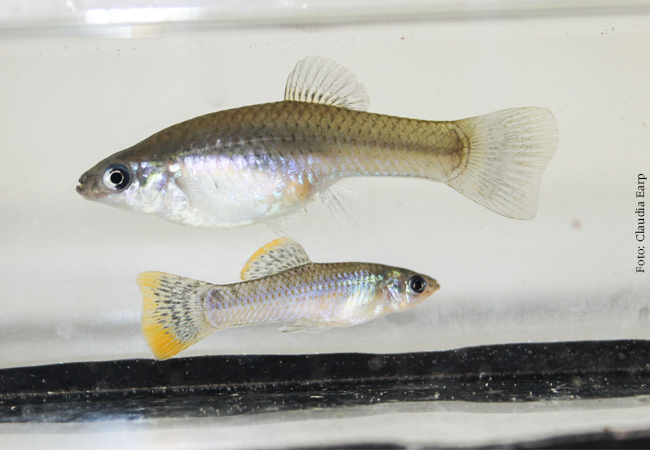

Pet owners have been sure of this for long time, and scientific research provides confirmation: animals, too, have personalities. A
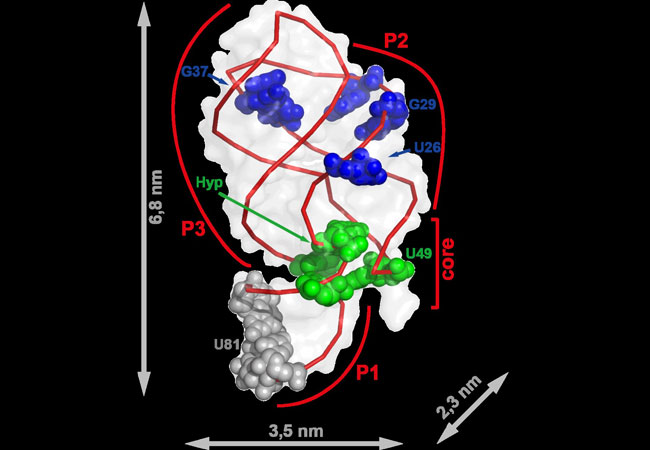
Plants use their roots to search for water. While the main root digs downwards, a large number of fine lateral
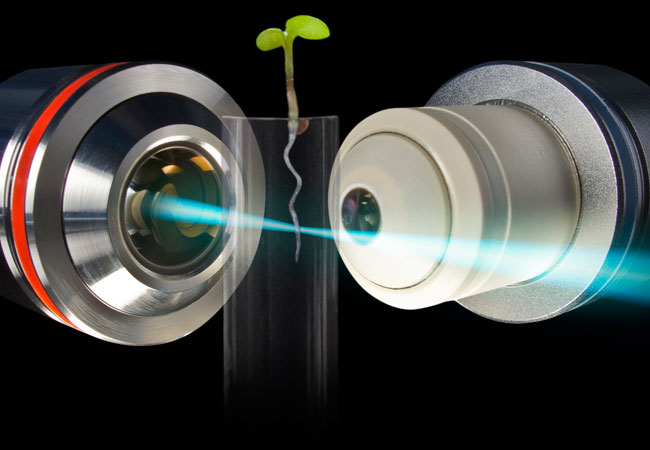
FRANKFURT. Even more detailed insights into the cell will be possible in future with the help of a new development
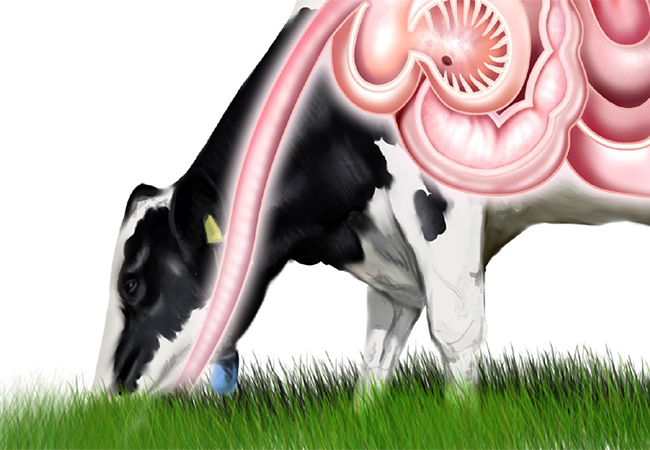
Cows can adapt themselves to a fluctuating sodium content in their feed. How they do that was so far a
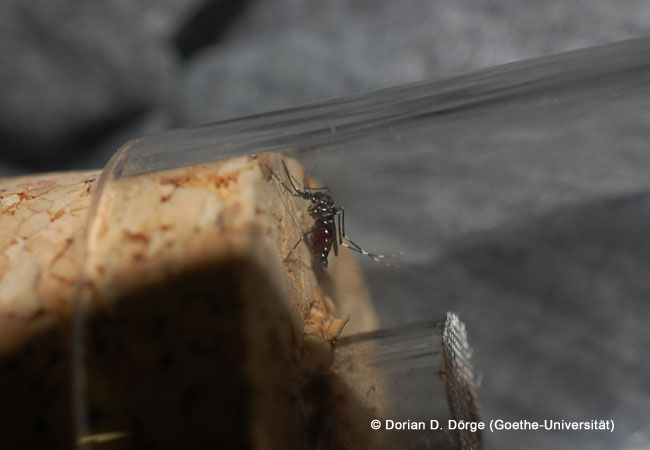

Scientists from Goethe University and Senckenberg Society for Nature Research are developing maps on the Zika virus infection risk The
You cannot copy content of this page