Bacteria act in groups to accomplish feats that are impossible to achieve if a single bacterium acts alone. For example, pathogenic bacteria act collectively to synthesize toxins to attack the host and to encase themselves in a shield that protects them from the host immune system and allows them to resist antibiotic treatment. To do this, bacteria communicate with each other with chemical “words”, count their numbers, and act in synchrony when they have sufficient cell numbers for success. The award winners have discovered the dictionary and syntax underlying bacterial communication, opening up new and unprecedented opportunities to fight bacterial infections.
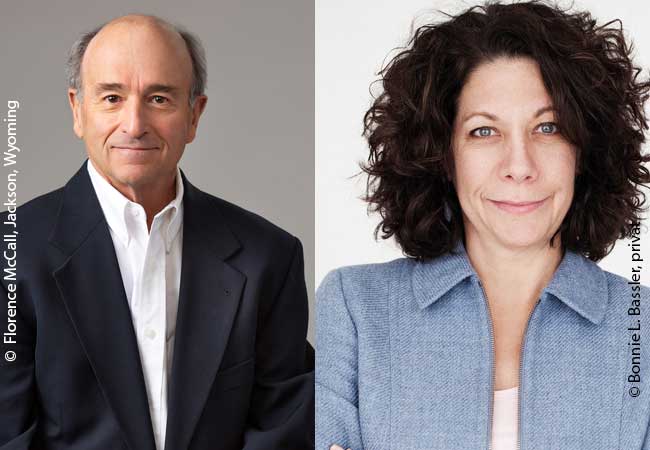
Two American scientists, Bonnie L. Bassler and Michael R. Silverman, receive the 2021 Paul Ehrlich and Ludwig Darmstaedter Prize, which is endowed with 120,000 €. Bassler is Professor at Princeton University and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator, Michael R. Silverman is Emeritus Professor of the Agouron Institute in La Jolla. The two researchers are honoured for their ground-breaking discoveries concerning bacterial „quorum sensing“, which refers to sophisticated systems of cell-to-cell communication that bacteria use to coordinate group behaviours. The award ceremony in St. Paul’s Church, which is traditionally held on March 14, Paul Ehrlich’s birthday, has been postponed due to the Coronavirus pandemic. Instead, Bassler and Silverman will receive the award at the ceremony in 2022.
„Silverman and Bassler have shown that, as for multicellular organisms, collective behaviour is the rule among bacteria, rather than the exception,“ wrote the Scientific Council in substantiating its decision. „Bacteria talk to each other, they eavesdrop on other bacteria, and they may even join forces. But: This ubiquitous chitchat, whose molecular underpinnings were discovered by Bassler and Silverman, also represents a previously unappreciated Achilles‘ heel in combating harmful microbes. Instead of killing bacteria with antibiotics, substances may be developed that interfere with bacterial communication effectively reducing their collective fitness. The prize-winners’ research thus has considerable relevance for medicine”.
Bacteria are extremely communicative. They send and receive chemical messages to find out whether they are alone or if additional members of their or other species are present in the vicinal community. To take a census of cell numbers, bacteria produce and release chemical signal molecules that accumulate in step with increasing cell numbers. When a threshold level of the chemical signal is achieved, the bacteria detect its presence. In response to it, in unison, bacteria undertake behaviours that are only productive when carried out in synchrony by the group, but not when enacted by a single bacterium acting in isolation. This chemical communication process is called quorum sensing and it controls hundreds of collective activities across the bacterial kingdom.
In the 1980s, Silverman discovered the first quorum-sensing circuit in the bioluminescent marine bacterium Vibrio fischeri. He identified the genes and proteins enabling production and detection of the extracellular signal molecule. He defined how the components functioned to promote collective behaviour. In the case of Vibrio fischeri, group-wide behaviour is the production of blue-green bioluminescence. Today, we know that quorum sensing is the norm in the bacterial world. Indeed, there are thousands of bacterial species that possess genes nearly identical to those discovered by Silverman. In all of these cases, these components allow bacteria to engage in group behaviours.
In the early 1990s, Bonnie Bassler proved that bacteria were “multilingual” and that they conversed with multiple chemical signal molecules. One communication molecule that Bassler discovered and named autoinducer- 2 enables bacteria to communicate across species boundaries. She went on to demonstrate that bacteria use quorum-sensing-mediated communication to differentiate self from other, showing that a sophisticated trait thought to be the purview of higher organisms, in fact, evolved in bacteria billions of years ago. In recent years, Bassler has shown that quorum sensing transcends kingdom boundaries as viruses and host cells, including human cells, engage in this ubiquitous chit-chat. She and other researchers also demonstrated that pathogenic bacteria rely on quorum sensing to be virulent. Bassler developed anti-quorum-sensing strategies that, in animal models, halt infection from bacterial pathogens of global significance.
“The full significance of the discoveries of the two laureates for microbiology and medicine has only recently been recognized,“ says Professor Thomas Boehm, Director at the Max Planck Institute for Immunobiology and Epigenetic and Chairman of the Scientific Council. „Decades of meticulous and painstaking work, showed that essentially all bacteria master the art of cell-to-cell communication,“ says Boehm. „What began with work on Vibrio fischeri and Vibro harveyi led to a fundamental change in perspective in bacteriology, and now opens up new and unprecedented opportunities in dealing with antibiotic resistance“.
Short biography Professor Dr. Bonnie L. Bassler Ph.D. (58).
Bonnie Bassler is a microbiologist. She studied biochemistry at the University of California at Davis and received her Ph.D. from the Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore. She joined the laboratory of Michael Silverman at the Agouron Institute in La Jolla as a postdoctoral fellow in 1990. She has been at Princeton University since 1994. Bonnie Bassler is a member of the National Academy of Sciences, the National Academy of Medicine, and the Royal Society. She is a researcher at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Squibb Professor and Chair of the Department of Molecular Biology at Princeton University. President Obama appointed her to a six-year term on the United States National Science Board. She has received more than twenty prestigious national and international awards.
Short biography Professor Michael R. Silverman, Ph.D. (77)
Michael Silverman is a microbiologist. He studied chemistry and bacteriology at the University of Nebraska at Lincoln and received his Ph.D. in 1972 from the University of California at San Diego. During the period from 1972-1982, Silverman made seminal contributions to the understanding of bacterial motility and chemotaxis. From 1982 until his retirement, he worked at the Agouron Institute in La Jolla, of which he is a co-founder.
The Paul Ehrlich and Ludwig Darmstaedter Prize
The Paul Ehrlich and Ludwig Darmstaedter Prize is traditionally awarded on Paul Ehrlich’s birthday, March 14, in the Paulskirche, Frankfurt. It honors scientists who have made significant contributions in Paul Ehrlich’s field of research, in particular immunology, cancer research, microbiology, and chemotherapy. The Prize, which has been awarded since 1952, is financed by the German Federal Ministry of Health, the State of Hesse, the German association of research-based pharmaceutical company vfa e.V. and specially earmarked donations from the following companies, foundations and organizations: Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung, Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH, C.H. Boehringer Pharma GmbH & Co. KG, Biotest AG, Hans und Wolfgang Schleussner-Stiftung, Fresenius SE & Co. KGaA, F. Hoffmann-LaRoche Ltd., Grünenthal GmbH, Janssen-Cilag GmbH, Merck KGaA, Bayer AG, Holtzbrinck Publishing Group, AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG, die Baden-Württembergische Bank, B. Metzler seel. Sohn & Co. and Goethe-Universität. The prizewinners are selected by the Scientific Council of the Paul Ehrlich Foundation.
The Paul Ehrlich Foundation
The Paul Ehrlich Foundation is a legally dependent foundation which is managed in a fiduciary capacity by the Association of Friends and Sponsors of the Goethe University, Frankfurt. The Honorary Chairman of the Foundation, which was established by Hedwig Ehrlich in 1929, is Professor Dr. Katja Becker, president of the German Research Foundation, who also appoints the elected members of the Scientific Council and the Board of Trustees. The Chairman of the Scientific Council is Professor Thomas Boehm, Director at the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg, the Chair of the Board of Trustees is Professor Dr. Jochen Maas, Head of Research and Development and Member of the Management Board, Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH. Professor Wilhelm Bender, in his function as Chair of the Association of Friends and Sponsors of the Goethe University, is Member of the Scientific Council. The President of the Goethe University is at the same time a member of the Board of Trustees.
Further information
You can obtain selected publications, the list of publications and a photograph of the laureate from Dr. Hildegard Kaulen, phone: +49 (0)6122/52718, email: h.k@kaulen-wissenschaft.de and at www.paul-ehrlich-stiftung.de