How oxygen radicals protect against cancer
Oxygen radicals in the body are generally considered dangerous because they can trigger something called oxidative stress, which is associated

Oxygen radicals in the body are generally considered dangerous because they can trigger something called oxidative stress, which is associated
Research from the University of Kent, Goethe-University in Frankfurt am Main, and the Philipps-University in Marburg has provided crucial insights
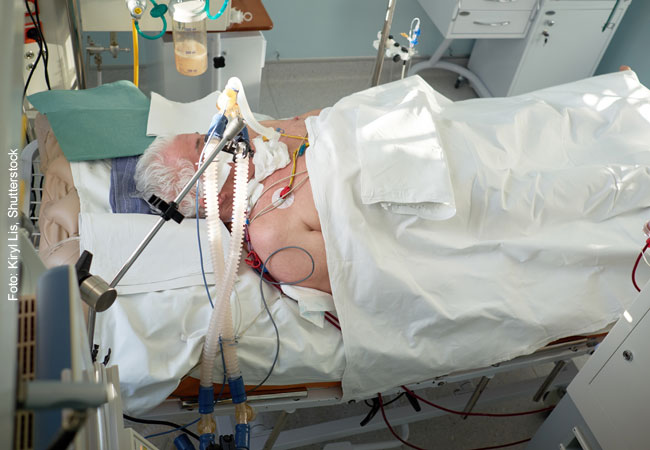
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is a common cause of death in patients with cirrhosis. In ACLF the progressive loss of

In order for the SARS-CoV2 virus to enter host cells, its “spike” protein has to be cleaved by the cell’s
Two young chemists at Goethe University want to develop highly effective vaccines using the carrier protein dodecin. To develop their

About ten percent of Parkinson’s cases can be ascribed to mutations in the LRRK2 gene. Five research teams from the

When the body can no longer compensate the gradual failure of the liver caused by liver cirrhosis, there is a
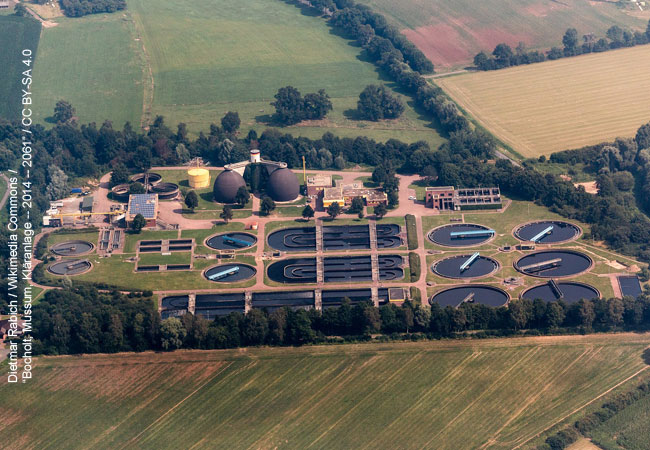

Since the beginning of the pandemic, research groups have been working on methods to detect SARS-CoV-2 viruses in wastewater to
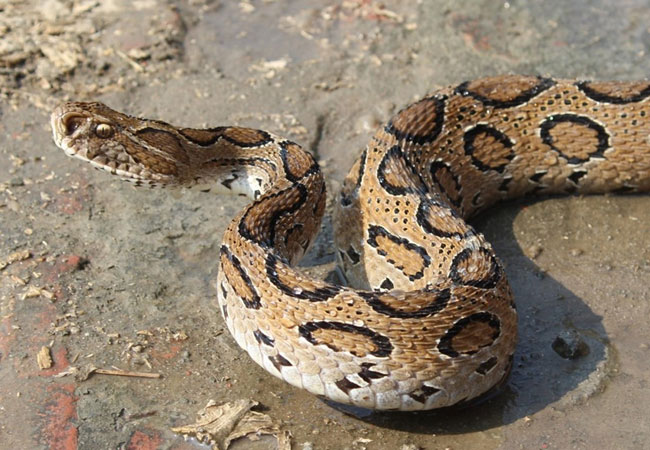

In cooperation with East Yangon University in Myanmar and the Max-Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena, researchers at Goethe
CARE (Corona Accelerated R&D in Europe), supported by Europe’s Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI), is the largest undertaking of its kind
The Institute of Medical Virology at Goethe-University, Frankfurt am Main, Germany, and the University of Kent’s School of Biosciences (UK)

Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is the most common kind of cancer in children. T-ALL, a subtype that resembles T-lymphocytes, can
Speaking requires both sides of the brain. Each hemisphere takes over a part of the complex task of forming sounds,

A team of biochemists and virologists at Goethe University and the Frankfurt University Hospital were able to observe how human

Goethe University and University Hospital Frankfurt donation barometer increases to 1.35 million euros – smallest individual donation of 2 cents
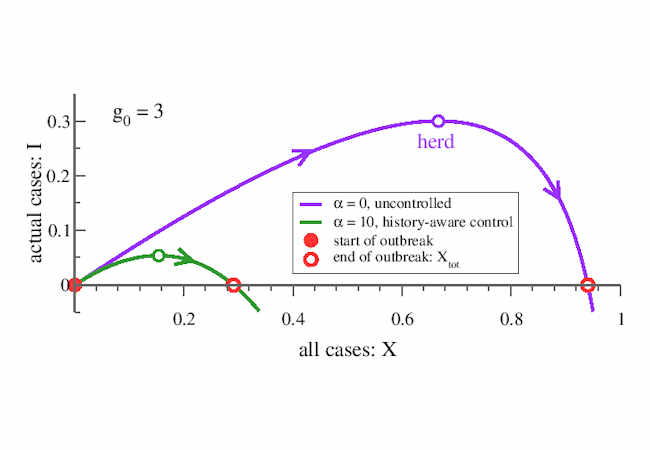
The governmental decision on when to loosen social distancing measures should not only depend on the latest number of cases.

The target is € 5 million and € 1 million have already been firmly pledged: The donation appeal launched just
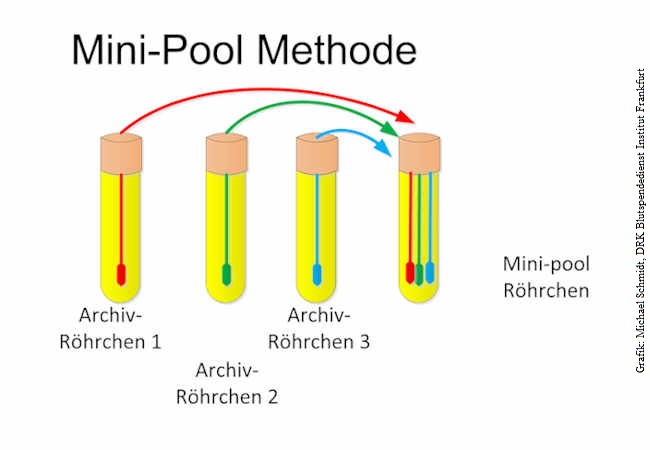
Researchers at the German Red Cross Blood Donor Service in Frankfurt headed by Professor Erhard Seifried, and the Institute for

Goethe University and University Hospital Frankfurt ask for funding for research, equipment and patient care At least five million euros

Attack or peacekeeping? Immune cells answer this question countless times a day. If they regularly missed the mark, it would
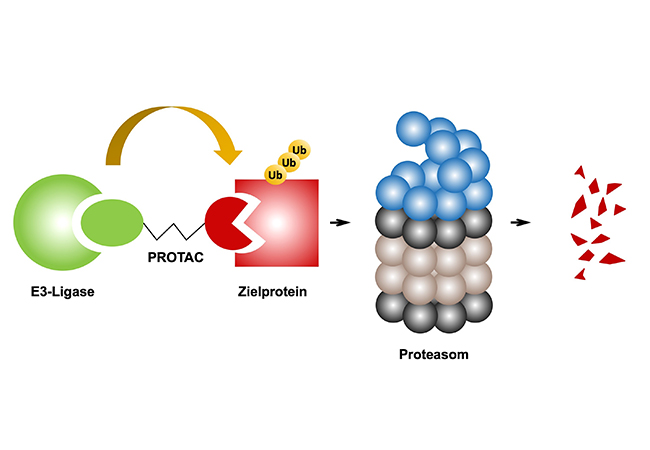
PROXIDRUGS, the regional network led by Goethe University, aims at developing active molecules for selective intervention, opening new therapeutic avenues.

Whether a sick cell dies, divides, or travels through the body is regulated by a sophisticated interplay of signal molecules
When cells are stressed, they initiate a complex and precisely regulated response to prevent permanent damage. One of the immediate
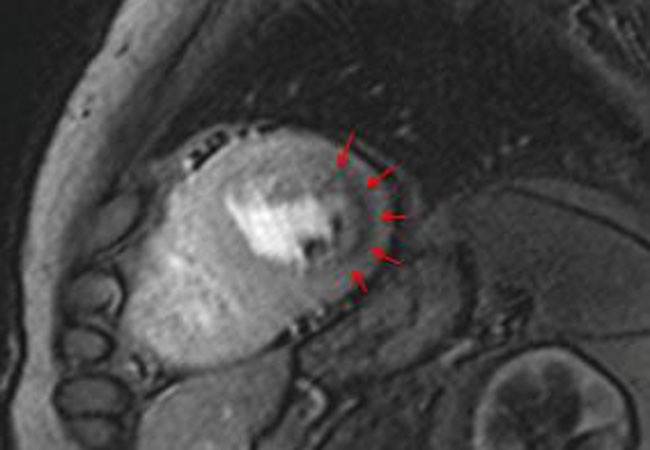
The non-invasive measurement of blood flow to the heart using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is on par with cardiac catheterization.

Goethe University and TU Munich have jointly obtained a new Collaborative Research Centre (Sonderforschungsbereich – SFB), which will receive approximately

Professor Ivan Dikic, Director of the Institute of Biochemistry II, has been elected to the venerable American Academy of Arts
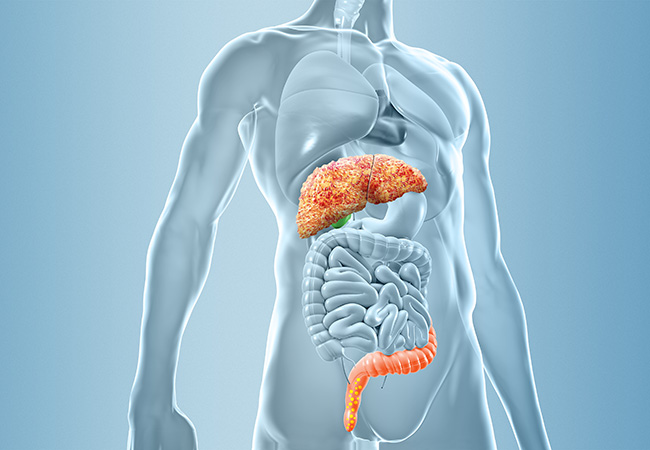
Albumin in high doses improves cardiac function and reduces inflammation Decompensated cirrhosis is a chronic disease linked to numerous complications

Professor Ferdinand Gerlach, Director of the Institute of General Practice at Goethe University, has received the Alfons and Gertrude Kassel
© 2023 Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main | Impressum | Datenschutzerklärung | Cookies verwalten
You cannot copy content of this page